Trend of Revit modeling for Architectural Design

In the global architectural market, design efficiency, precision and cost management are the most important factors to consider for an architect. The growing demand of complex design and controlling project cost and time overruns sheds some pressure on design professionals for ensuring streamlined construction management.
The modern architectural practices eliminate the use of obsolete 2D AutoCAD plans for design planning and coordination. Revit modeling for architectural design has proven to be a great tool not only for effective design development, planning and coordination but also for construction management. There are many factors that make Revit 3D Modeling for architectural design a preferred choice for architects all around the globe.
In this article, we will discuss how architects use revit for building design, architectural workflow in revit, and maximizing design potential using 3D Revit modeling.
How Architects Use Revit for Building Design
Revit modeling for architectural design offers wide range of tools that brings efficiency and precision in architectural workflow. During their daily work, architects utilize Revit for building design, development, and coordinating tasks. Below are some of the important domains in which architects use Revit Modeling for Architectural Design:
1. Architectural Drawings and Annotations
The beauty of Revit for building design lies in its ability to automatically generate floor plans, sections, elevations, and detailed drawings directly from the 3D model while developing an architectural model using a predefined library of architectural elements.
Unlike AutoCAD, where each section and elevation must be drafted manually, Revit automates the creation of these views. Because of this automation, architects choose to use Revit for building design because it increases precision and saves a lot of time during drafting and annotating.
2. Building Information Modeling (BIM)
Revit is a BIM software that enables architects to create a detailed 3D model of a building, which includes not only the geometry but also data about materials, components, and construction processes.
Depending on the level of detail (LOD)—such as LOD 300, 400, or 500/As-built—architects can populate the necessary design information directly into the Revit model. This makes the Revit model ready for various stages of construction, including facilities management.
3. Project Management
Revit plays a crucial role in project management by empowering architects to develop comprehensive construction schedules that outline key milestones and deadlines. This functionality allows architects to track project progress in real time, ensuring that all team members are aligned and informed.
Furthermore, Revit modeling for architectural design enables architects to plan for different phases of the project, facilitating better resource allocation and time management. Revit for building design also has the ability to link the model to advanced cost estimation tools. This integration allows architects to generate accurate budgets based on real-time data from the 3D model.
By continuously monitoring costs throughout the project lifecycle, architects can identify potential budget overruns early and make necessary adjustments to keep the project on track.
Understanding Architectural Workflow in Revit
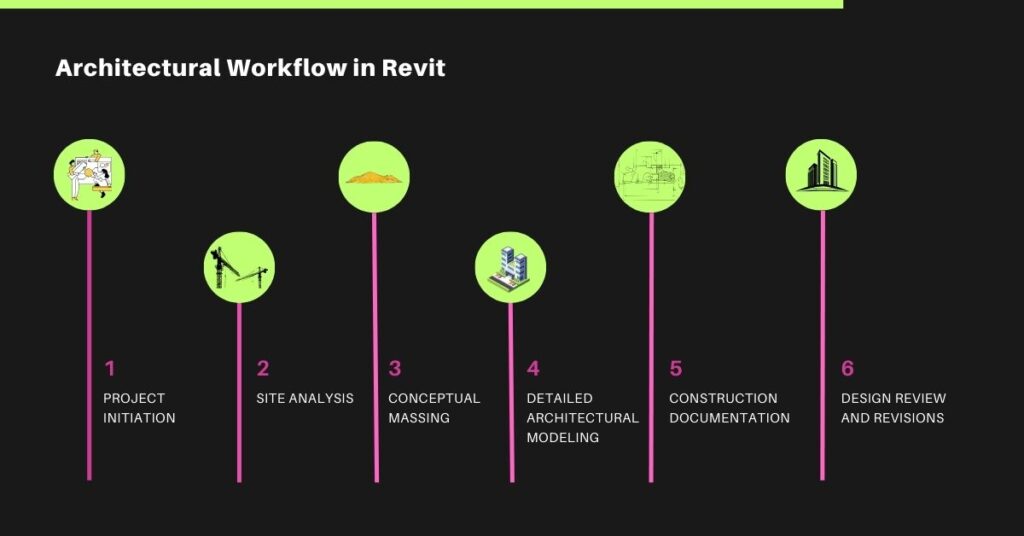
1. Project Initiation
Architects begin by setting up a new project in Revit, selecting the appropriate architectural template. They establish key project parameters, such as units of measurement and project location, creating a structured foundation for their design efforts as their first step in architectural workflow in revit.
2. Site Context and Analysis
Next, architects import site surveys and topographical data to gain a comprehensive understanding of the project context. Utilizing Revit’s site analysis tools, they conduct solar orientation studies and assess the site’s characteristics, which inform crucial design decisions.
3. Conceptual Massing
With the site context in mind, architects explore various forms and volumes using Revit’s massing tools. They create massing models to visualize initial design concepts, allowing for quick iterations that help evaluate zoning constraints and potential environmental impacts.
4. Detailed Architectural Modeling
Once a clear massing strategy is established, architects transition to detailed modeling by incorporating elements like walls, floors, roofs, and curtain walls. They may also create or modify custom families in the family editor, ensuring that every component aligns with the overall design intent.
5. Integration of Structural and MEP Models
Architects work closely with structural and MEP engineers throughout the design process, incorporating their models into the Revit project. This collaboration in Revit modeling for architectural design is essential for conducting clash detection, which helps identify and resolve conflicts early in the design phase.
6. Construction Documentation
By enabling architects to build comprehensive floor plans, sections, elevations, and schedules directly from the model, Revit modeling for architectural design expedites the creation of construction documentation. This ensures that documentation is accurate and compliant with industry standards and local building codes.
7. Design Review and Revisions
Throughout the project, architects engage in design reviews with clients and team members, using Revit’s markup tools to gather feedback. They make revisions as needed, benefiting from Revit’s parametric features that ensure all elements remain synchronized.
Also read: Convert Point Cloud to Revit Model
How Architects Maximize Design Potential with Revit modeling
While we discussed why architects use revit for building design and architectural workflow in Revit, now lets dive in some of the great features in Revit take maximize overall design potential for architects and designers:
1. Using Revit for Conceptual Architectural Designs
Using Revit’s massing tools, architects may swiftly visualize spatial relationships and forms while exploring conceptual concepts. Iterative modeling in 3D Revit encourages innovation. This enables architects to test various design ideas and refine concepts based on immediate feedback.
By generating massing models, architects make informed decisions early, setting the stage for successful project development.
2. Revit Customization Architectural Projects
With the many customization options Revit modeling provides, architects can modify their workflows to satisfy project requirements.
By adjusting templates, parameters, and settings, architects can create a personalized environment that enhances efficiency and aligns with design standards. This adaptability in Revit modeling process not only streamlines the design process but also ensures consistency across projects, improving overall productivity.
3. Creating Architectural Families in Revit
Architects can create custom families in Revit to represent unique building components, ensuring their designs accurately reflect intended materials and aesthetics.
This capability in Revit modeling for architectural design allows for greater flexibility in design, as architects can develop specific elements tailored to their projects. By utilizing Revit families’ models, they maintain design integrity and ensure seamless integration within the overall model.
4. Architectural Rendering in Revit for Presentation
With the help of Revit’s rendering features, architects can create stunning visualizations that clearly convey their design purpose to stakeholders and clients.
By creating realistic 3D Revit Model renderings, architects showcase materials, lighting, and spatial relationships, bringing their designs to life. These compelling presentations not only facilitate better understanding but also enhance the decision-making process, ultimately leading to successful project outcomes.
Conclusion
In today’s architectural landscape, Revit modeling for architectural design has become essential for enhancing design efficiency and collaboration. This blog highlighted how Revit empowers architects to transition from traditional 2D methods to a dynamic 3D environment, automating the generation of drawings and facilitating detailed modeling.
By allowing customization and the creation of architectural families, Revit modeling enhances creativity and ensures designs align with project needs. Furthermore, its rendering capabilities enable architects to produce high-quality visualizations, improving client communication and decision-making.
As architects continue to embrace Revit modeling for architectural design, they not only streamline workflows but also elevate project quality, positioning themselves for success in an increasingly complex building environment. Embracing Revit is a strategic move toward architectural excellence.
